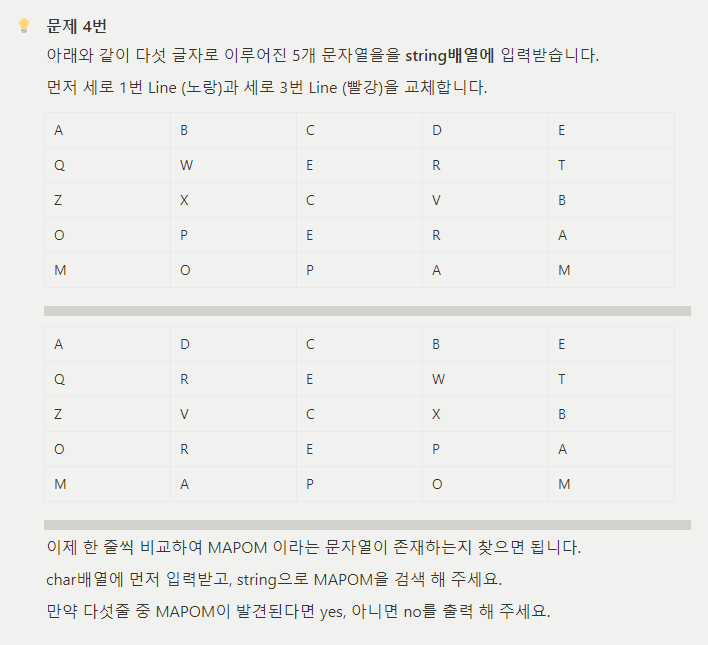
더보기




#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Set
{
int num;
char c;
};
void InsetSort(vector<Set>& set)
{
int size = set.size();
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++)
{
int numData = set[i].num;
char cData = set[i].c;
int j;
for ( j = i - 1; j >= 0 ; j--)
{
if (set[j].num == numData)
{
if (set[j].c > cData)
{
set[j + 1].c = set[j].c;
set[j + 1].num = set[j].num;
}
else
break;
}
else if (set[j].num > numData)
{
set[j + 1].c = set[j].c;
set[j + 1].num = set[j].num;
}
else
break;
}
set[j+1].num = numData;
set[j+1].c = cData;
}
}
int main()
{
vector<Set> set;
int a;
cin >> a;
for (size_t i = 0; i < a; i++)
{
int num;
char c;
cin >> num >> c;
set.push_back({ num , c});
}
InsetSort(set);
//만약 람다를 사용한다면
/*sort(set.begin(), set.end(), [&](const Set& a, const Set& b)
{
if (a.num == b.num) return a.c < b.c;
return a.num < b.num;
});*/
for (const auto& s : set)
{
cout << s.num << s.c << endl;
}
return 0;
}
더보기



#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 4;
const int strMAX = 3;
int arr[4] = { 0,0,0,0 };
string str[strMAX] = { "금", "은", "동" };
void InsertSort(int score)
{
const int last = MAX - 1;
if (arr[last] < score)
arr[last] = score;
else
return;
int data = arr[MAX - 1];
int j;
for (j = last - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (arr[j] < data)
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
else
break;
}
arr[j + 1] = data;
}
int main()
{
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int score;
cin >> score;
InsertSort(score);
}
for (int i = 0; i < strMAX; i++)
{
cout << str[i] << arr[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
더보기
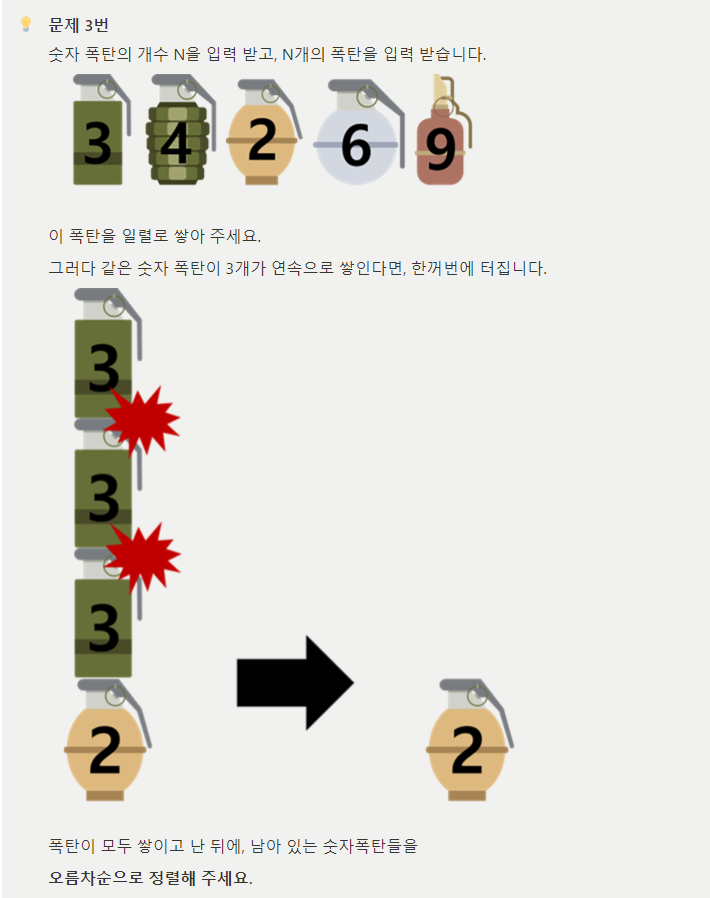



#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int first = 1;
const int boom = 3;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
int N;
cin >> N;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int num;
cin >> num;
if (v.size() != 0 && v.back() != num)
count = 1;
else
count++;
if (count == boom)
{
while (count > first)
{
v.pop_back();
count--;
}
count = 0;
}
else
{
v.push_back(num);
}
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
더보기


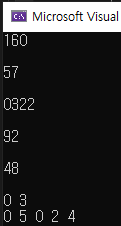


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<vector<int>> v;
v.resize(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
string strNUm;
cin >> strNUm;
for (int j = 0; j < strNUm.size(); j++)
{
int num = strNUm[j] - '0';
v[i].push_back(num);
}
}
int line1, line2;
cin >> line1 >> line2;
sort(v[line1].begin(), v[line1].end());
sort(v[line2].begin(), v[line2].end());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i][0] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
더보기


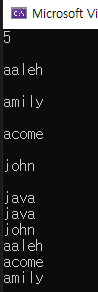


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<string> names;
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
string name;
cin >> name;
names.push_back(name);
}
sort(names.begin(), names.end(), [&](const string& name1, const string& name2)
{
if (name1.size() == name2.size())
{
return name1 < name2;
}
return name1.size() < name2.size();
});
for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); i++)
{
cout << names[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
더보기

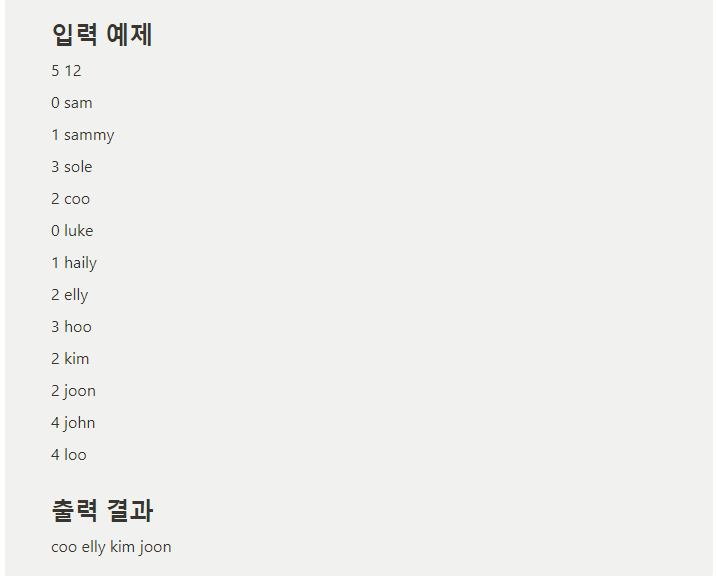
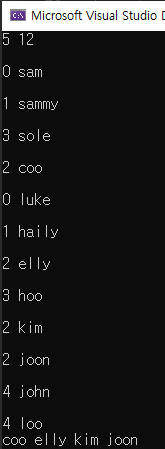


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Vote
{
int num;
string name;
};
int main()
{
vector<vector<Vote>> info;
int num;
int people;
cin >> num >> people;
info.resize(num);
for (int i = 0; i < people; i++)
{
int num;
string name;
cin >> num >> name;
info[num].push_back({num, name});
}
sort(info.begin(), info.end(), [&](const vector<Vote>& a, const vector<Vote>& b)
{
return a.size() > b.size();
});
for (int i = 0; i < info[0].size(); i++)
{
cout << info[0][i].name << " ";
}
return 0;
}
더보기

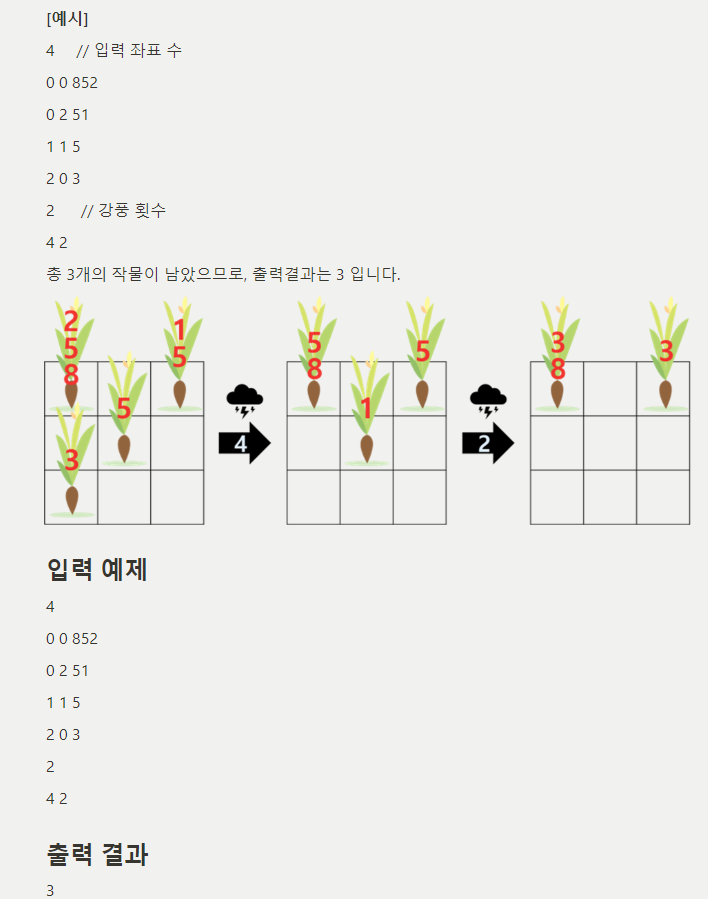


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<vector<string>> farm(3, vector<string>(3));
vector<pair<int, int>> xy;
int crops = 0;
int N,K;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int x;
int y;
string amount;
cin >> x >> y >> amount;
farm[x][y] = amount;
xy.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
crops += amount.size();
}
cin >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++)
{
int pow;
cin >> pow;
for (int j = 0; j < xy.size(); j++)
{
int x = xy[j].first;
int y = xy[j].second;
if (farm[x][y] == "")
continue;
int amount = farm[x][y].back() - '0';
if (pow > amount)
{
farm[x][y].pop_back();
crops--;
}
else
{
int _amount = stoi(farm[x][y]) - pow;
farm[x][y] = to_string(_amount);
}
}
}
cout << crops;
return 0;
}
더보기
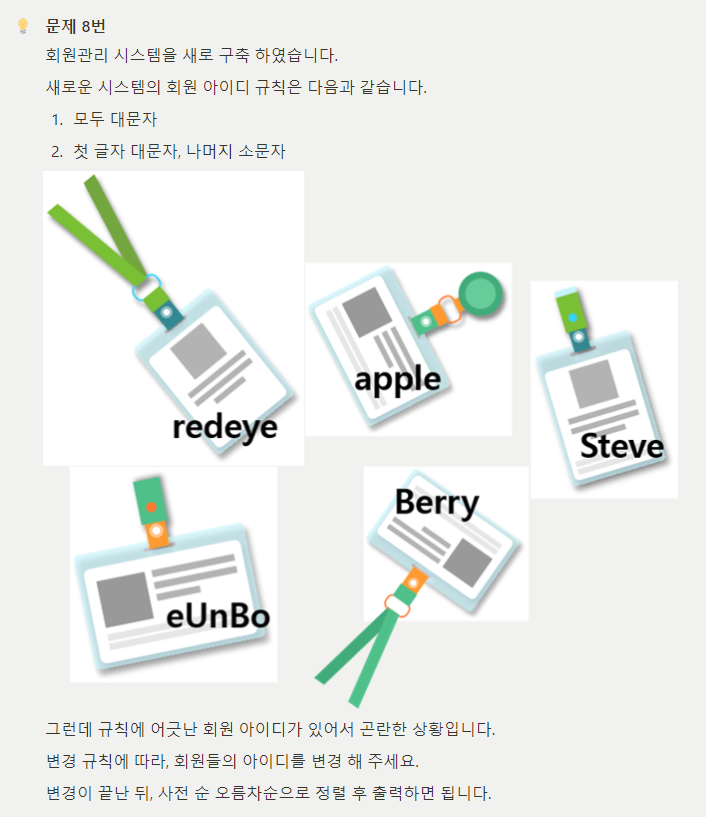



#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool IsLowerOnly(const string& str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
bool _isupper = isupper(str[i]);
if (_isupper)
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool IsUpperHeadOnly(const string& str)
{
for (int i = 1; i < str.size(); i++)
{
bool _isupper = isupper(str[i]);
if (_isupper)
return false;
}
return true;
}
void ToUpperAllIndex(string& str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
str[i] = toupper(str[i]);
}
}
void FixName(vector<string>& names)
{
int size = static_cast<int>(names.size());
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (IsLowerOnly(names[i]))
names[i][0] = toupper(names[i][0]);
else if (!IsUpperHeadOnly(names[i]))
ToUpperAllIndex(names[i]);
}
}
더보기


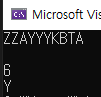


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<char> alpha;
int select;
alpha.resize(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cin >> alpha[i];
}
cin >> select;
sort(alpha.begin(), alpha.end(), [&](const char& a, const char& b)
{
return a < b;
});
const int ASCll = 128;
int alphaAmount[ASCll] = {};
int size = alpha.size() - 1;
for(int i = size; i > (size - select); i--)
{
const int toNum = alpha[i];
alphaAmount[toNum]++;
}
int g_alpha = -1;
char most;
for (int i = 0; i < ASCll; i++)
{
if (alphaAmount[i] > g_alpha)
{
g_alpha = alphaAmount[i];
most = i;
}
}
cout << most;
return 0;
}
더보기



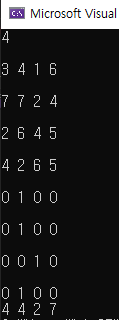



#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<vector<int>> number;
vector<vector<int>> bit;
vector<pair<int, int>> xy;
int n;
cin >> n;
number.resize(n);
bit.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int num;
cin >> num;
number[i].push_back(num);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int _bit;
cin >> _bit;
bit[i].push_back(_bit);
if (_bit == 1)
xy.push_back(make_pair(i,j));
}
}
const int size = xy.size();
vector<vector<int>> priority(10);
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
int x = xy[i].first;
int y = xy[i].second;
priority[number[x][y]].push_back(number[x][y]);
}
sort(priority.begin(), priority.end(), [&](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b)
{
if (a.size() == b.size() && !a.empty() && !b.empty())
return a[0] < b[0];
else
return a.size() > b.size();
});
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
const int length = priority[i].size();
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++)
{
cout << priority[i][j] << " ";
}
if (priority[i].size() == 0)
break;
}
return 0;
}
더보기

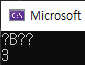

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 6;
string dictionary[MAX] =
{
"ABCD",
"ABCE",
"AGEH",
"EIEI",
"FEQE",
"ABAD"
};
int Search(string& str)
{
vector<int> index;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] != '?')
index.push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
bool success = true;
string word = dictionary[i];
for (int j = 0; j < index.size(); j++)
{
if (word[index[j]] != str[index[j]])
success = false;
}
if (success)
count++;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
int result = Search(str);
cout << result;
return 0;
}
더보기

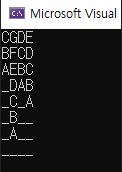

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
int count = 0;
while (true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] == '_')
{
cout << str[i];
continue;
}
str[i]--;
if (str[i] < 'A')
{
str[i] = '_';
count++;
}
cout << str[i];
}
cout << endl;
if (count >= str.size())
break;
}
return 0;
}
더보기
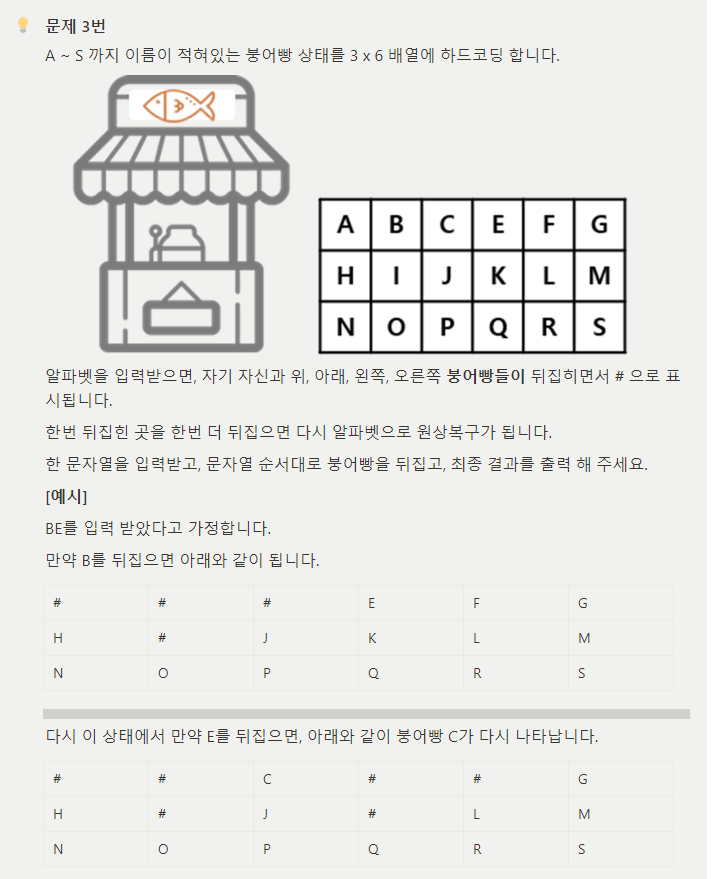



#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<char>> tile =
{
{'A','B','C','E','F','G'},
{'H','I','J','K','L','M'},
{'N','O','P','Q','R','S'},
};
vector<vector<char>> cpy_tile =
{
{'A','B','C','E','F','G'},
{'H','I','J','K','L','M'},
{'N','O','P','Q','R','S'},
};
bool Flip(int y, int x)
{
int dy[] = {-1,1,0,0};
int dx[] = {0,0,-1,1};
tile[y][x] = '#';
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int ny = y + dx[i];
int nx = x + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx > tile[0].size() - 1 || ny > tile.size() - 1)
continue;
if (tile[ny][nx] == '#')
tile[ny][nx] = cpy_tile[ny][nx];
else
tile[ny][nx] = '#';
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
char c = str[i];
for (int j = 0; j < tile.size(); j++)
{
bool done = false;
for (int k = 0; k < tile[0].size(); k++)
{
if (c == tile[j][k])
{
done = Flip(j, k);
break;
}
}
if (done)
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < tile.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < tile[i].size(); j++)
{
cout << tile[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
더보기



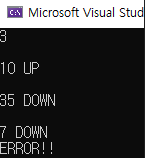
예시2
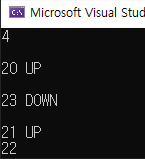
예시3



#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int people;
int n;
string updown;
cin >> people;
int first = 0;
int tail = 50;
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < people; i++)
{
cin >> n >> updown;
if ("UP" == updown)
{
first = n + 1;
}
else if ("DOWN" == updown)
{
tail = n - 1;
}
if (first == tail)
{
flag = 1;
cout << first;
break;
}
else if(first > tail)
{
flag = 1;
cout << "ERROR!!";
break;
}
}
if(flag == 0)
cout << first << " ~ " << tail;
return 0;
}


더보기



#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void Chase(vector<pair<int, string>>& info, int index)
{
if (info[index].second == "테러범")
{
cout << index << "번" << endl;
return;
}
int dir = 1;
if (info[index].second == "<<")
dir *= -1;
int nextIndex = index + (info[index].first * dir);
Chase(info, nextIndex);
cout << index << "번" << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<pair<int, string>> info =
{
{3, ">>"}, {2, ">>"}, {1, "<<"}, {3, ">>"}, {2, "<<"}, {0, "테러범"}, {1, "<<"}
};
int index;
cin >> index;
Chase(info, index);
return 0;
}
더보기

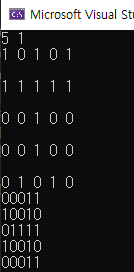
1회 회전
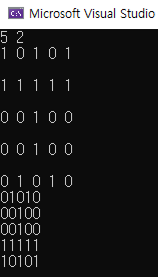
2회 회전


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 10;
int arr[MAX][MAX];
int cpyarr[MAX][MAX];
void Rotat(int num)
{
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < num; j++)
{
cpyarr[j][num - 1 - i] = arr[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < num; j++)
{
arr[i][j] = cpyarr[i][j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n, turn;
cin >> n >> turn;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cin >> arr[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < turn; i++)
{
Rotat(n);
int a = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cout<< cpyarr[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}

더보기


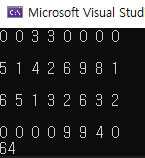


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int column = 4;
const int row = 8;
int ground[column][row];
bool visited[column][row];
int MakeArea(int y, int x)
{
int sum = 0;
int height = column;
int width = row - x;
int flag = 0;
for (int i = y; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
if (ground[i][x + j] == 0)
{
if (j == 0)//직사각형 아님
flag = 1;
width = j;//넓이 결정
break;
}
sum += ground[i][x + j];
visited[i][x + j] = true;
}
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < column; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++)
{
cin >> ground[i][j];
}
}
int max = -1;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < column; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++)
{
if (ground[i][j] != 0 && visited[i][j] == false)//이미 방문했다면 어떠한 직사각형에 포함이 된 상태기 때문에 계산할 필요x
sum = MakeArea(i, j);
max = sum > max ? sum : max;
}
}
cout << max;
return 0;
}